It is expected that by the year 2022, the entire motion control encoder global market is going to grow at a highly significant rate. Most of the major worldwide industries are going to be directly impacted by the growth. This includes industrial automation electronics, consumer electronics, aerospace, defense technology and chemical manufacturing, just to mention a few. Different major players are expected to be a part of the growth but this is something that can always change.
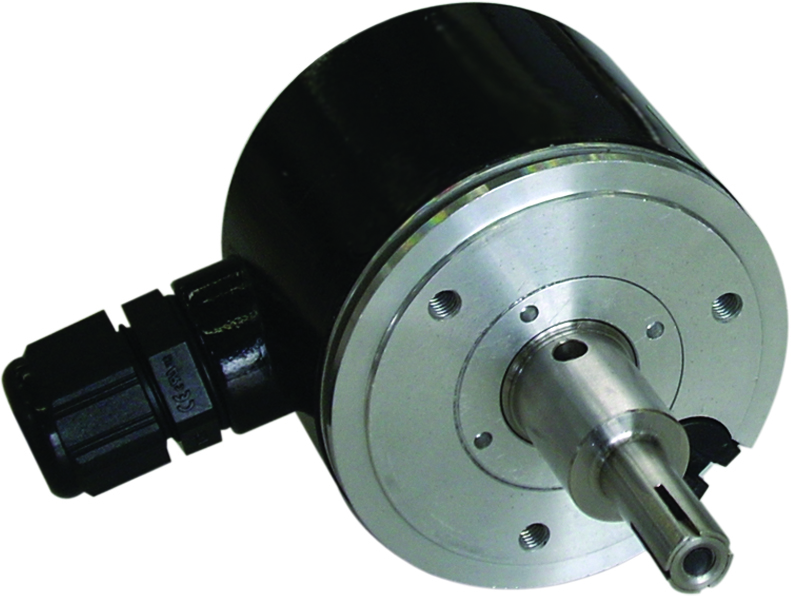
The rotary encoders are going to be connected to the shaft. When we have a shaft that rotates, encoders output pulses. The pulses are used by the system to determine an object’s speed. When the system works, pulse amounts are counted for a shaft turn. This allows the calculation of the resolution. The encoders used typically supply some square-wave signals in 2 channels offset or simply out of phase, at an angle of 90 degrees. Every single rotation increment will spur output signal.
Out of all the encoders that are used on the market at the moment, the two that are the most common are absolute encoders and incremental encoders. Choosing between the two is important when you want to create a good system that requires such parts. Some are better in some cases. In order to make the correct choice, here are some things that you have to be aware of.
Understanding Absolute Encoders
The big advantage of the rotary Rozum absolute encoder is the fact that unique position values are provided really fast. This happens as soon as the system is turned on as position is scanned and compared to an added coded element.
In the absolute encoder you can see an added encoder disc with slots or marks present on the power-transmission shaft, together with a stationary pickup. It is the disc that will record a completely unique code for absolutely every single shaft position. There is code for every single position and even the movements that happen when the system does not have power can be recorded into the accurate position values. This is possible when the absolute encoder is turned on.
Two absolute encoder types exist:
- Single-turn encoders
- Multi-turn encoders
The single-turn encoder is used to measure displacement across 360 degrees or in one full turn from the starting position. Output is simply repeated to get new readings. The multi-turn absolute encoder will measure the reading in a similar way. However, total revolution numbers are also tracked by using a word for every single position, together with the number of revolutions.
In the even that safety stands out as a concern for the system, the absolute rotary encoder is always preferred. This is because positioning happens just as the system has power. The single-turn encoder is good for the short travel situation. The multi-turn encoder is much better for longer poisoning cases that are more complex.
When you use multi-turn absolute encoders, position data is electronically recorded, usually as binary reading. Resistance to the presence of electrical noise is really high. However, the absolute encoder is more expensive than the incremental encoder.
Advantages Of Using Absolute Rotary Encoders:
-
In the event that a power outage happens, position is remembered. Continuous position monitoring thus becomes possible.
-
The encoders normally have functions like Fieldbus, speed, preset and scaling.
-
There are many interface options that are available and can be used, like serial, parallel, Fieldbus, Ethernet and analog.
-
You can determine the machine’s exact position at all times and you can control electronic data storage without difficulty.
-
There are the 2 options available, multi-turn and single-turn.
-
The measuring principle is magnetic or optical.
-
The resolution of the absolute encoder can go as high as 16 bits. This means 65,536 PPR (pulses per revolution).
Understanding Incremental Encoders
In the incremental encoder we have an output signal that is generated every single time a shaft rotates for a specific amount. Device resolution is simply defined by how many signals are present in a turn. Every single time that you power on the incremental encoder, counting starts from the zero number. This is regardless of the position of the shaft or the previously recorded position. You need this because a reference point is necessary. It has to be determined for absolutely all the positioning tasks. This includes the control system’s startup and whenever the power source was disrupted. The incremental encoders basically have to re-home to a reference point in the event that it is powered down.
The rotary incremental encoders are storing data in a counter or in the external buffer. Battery backup systems are included in most situations because of the fact that this removes the need to re-home after unplanned or planned shutdowns. An incremental encoder is quite simpler when you need to use it. Many systems also prefer them because of the fact that they are cheaper.
Advantages Of Incremental Rotary Encoders:
-
The encoders are really good in the event that simple pulse counting is needed or there are frequency monitoring applications that apply, like direction, position monitoring and speed.
-
The pulse count can be as high as 16,348 PPR.
-
The encoders are less complex and cost-effective when compared with the absolute encoder.
-
The system uses A, B, Z and even inverted signals as TTL or HTL.
-
The use of the magnetic measuring principle.
-
Scaling functionality is flexible.
-
The incremental encoders can have a resolution that will go as high as 50,000 PPR.
Conclusions
To sum up, these two encoder types are the most used at the moment. They are preferred in various situations. However, we can easily say that the absolute rotary encoders are better. They are used for operations that are much more complex when compared to the incremental rotary encoders.
When you choose the best encoder to use, make sure that you consider the advantages that were mentioned above. You need to be sure that your choice is a correct one and that you mainly think about the application that needs the encoder to be used. Usually, engineers make the final choice, based on application, budget and applicability.








![Watch Video Now on xiaohongshu.com [以色列Elevatione perfectio X美容仪 perfectio X 全新仪器黑科技了解下]](https://www.techburgeon.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/perfectiox-singapore-150x150.jpg)
