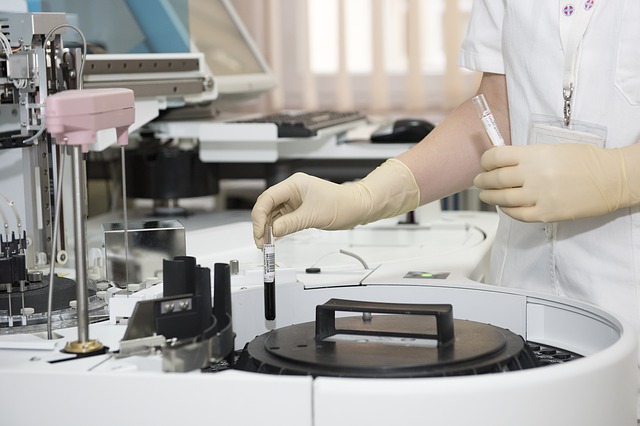

While technological innovation has helped the healthcare industry progress and various stakeholders stay connected in real-time, the convenience comes with a price. The risk of private data being compromised is now greater than ever. This poses a massive threat to the healthcare industry, where it is vital to protect patient data in order to avoid problems like medical identity theft and insurance fraud. In fact, even in case a data breach does not lead to serious crimes like these, a practice still has to deal with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) fines and other compliance costs, not to mention the reputational damage it suffers and the patient trust it may never get back.
Alarmingly, data breaches in the healthcare industry are not that uncommon. 2012 research shows that 94% of all healthcare organizations had gone through at least one data breach. In 2015, there were 229 breaches, affecting over 110 million patients. Because of this, it is not required of organizations to comply with safety standards in order to secure patient data. In general, there are two types of compliances required by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). While the required ones are compulsory of all healthcare providers, the addressable provisions are flexible since not all practices have the same resources.
The bottom line is, all hospitals and independent healthcare practices need to do their best to protect patient data. Here are the six best practices to secure healthcare data:
Risk Assessment
One of the most important steps a healthcare facility can take to protect patient data is to carry out an evaluation of the risks posed to the practice. While these will vary from practice to practice, some common risks include:
- Active infiltration by online hackers
- DDOS attacks on your server
- Theft or alteration of data by practice employees
- Viewing of confidential data by unauthorized personnel
- Losing data due to software/hardware failure or other issues
All these and other possible risks need to be identified, and then a contingency plan and policy needs to be designed in order to be able to cope with anything that might happen. Healthcare providers must also keep in mind that this is an on-going process and needs to be updated regularly according to technological or other changes.
Protect theNetworkand Wireless Connections
There are a number of ways that potential hackers can break into a healthcare facility’s system. It is therefore important to make sure that the primary internet connection and all other internet connections used to access private data are properly protected. Providers must also make sure that routers are always updated, their passwords are changed frequently, as unauthorized devices are not allowed to connect. A common mistake that healthcare professionals as well as IT specialists working in healthcare organizations make is investing in firewalls and anti-virus software systems only. An additional step that needs to be taken is to invest in tools that help reverse, control or contain damage in case a breach does occur despite protective systems installed.
Educate and Train Staff Members
As unfortunate as it is, practice staff members are often involved in data breaches, both with malicious intent and by mistake. To avoid both, it is important to regularly educate and train staff not only on the legal compliance standards they need to abide by, but also on the consequences and penalizations of data breaches. A little investment in training staff to handle confidential data correctly can save a practice hundreds of thousands of dollars potentially spent in case of a breach by a staff member. Some basic things that must be included in data protection training for employees are:
- What are HIPAA standards?
- What are HIPAA violations?
- What are the consequences of violations?
- How to avoid malicious attacks targeting employees?
- How to avoid phishing/social engineering targeting employees?
- How to choose secure passwords?
Create a Mobile Device Policy and Encrypt Devices
Since healthcare employees commonly use personal portable devices at work, it is important for a healthcare facility to write a mobile device policy to protect confidential data. This must include:
- What can be accessed from mobile devices
- Which wireless networks they can connect to within the facility
- What can be stored on mobile devices
- Which apps can be installed
- Forbidden networks/websites/applications
In addition, it is important to encrypt all portable devices within the healthcare facility that have any private data on them or a way to access private data. Previously, breaches have occurred by devices with important information being stolen. Computers, smartphones, tablets, USB drives, and any other devices that may hold patient data must be encrypted.
Implement Physical Controls to Protect Data
While EHR systems are becoming more and more common and are definitely recommended, there are practices that still hold some paper-based data, or are in the process of making the shift to electronic records. Any healthcare facility that has any physical patient data needs to ensure that it is protected with various measures, like physical locks, security cameras, security personnel, etc. Even if there is no paper data that needs to be protected, IT equipment needs to be secured by restricting access to server rooms, and using cable locks to secure office equipment like laptops.
Ensure Everyday Safety Practices
Often, breaches occur because practice staff overlooks everyday safety practices that should be part of habit. It may seem strange to reinforce these strategies since they comprise basic knowledge, but it is important to remember that some staff may have very basic IT skills and it is human nature to skip the most mundane of things sometimes. Here are important everyday practices to keep in mind:
- Choose strong passwords, including numbers and symbols
- Never choose easily guessable passwords like birthdate, name of a spouse, etc.
- Changes passwords and other login information regularly
- Do not use the same passwords for multiple platforms
- Remove unused/past accounts that are no longer needed
- Do not browse unsecured websites or applications
- Do not install unauthorized software
- Do not access private social media on work devices
- Do not use private devices like USB devices on work devices
- Never use outdated software
- Always check security standards, regardless of software reputation
Many healthcare data protection strategies may seem like a given, but it goes a long way to remember that it is often only one small mistake that can lead to a costly breach. It is better to be prepared than have to deal with consequences!









![Watch Video Now on xiaohongshu.com [以色列Elevatione perfectio X美容仪 perfectio X 全新仪器黑科技了解下]](https://www.techburgeon.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/perfectiox-singapore-150x150.jpg)
